
Probiotics | Super Foods |Benefits ,Usage and Types
Health benefits of probiotic bacteria.
- Reduce blood cholesterol
- Maintain intestinal health
- Alleviate intestinal bowel diseases
- Modulate immune system
- Reduce incidence of gastrointestinal infections
- Reduce incidence of urinary and vaginal infections
- Alleviate lactose intolerance
- Anti-carcinogenic and anti-tumorigenic
- Reduce incidence and severity of diarrheal diseases
Basics/Understanding the Gut world
Intestinal tract is home to one hundred trillion (1014) microorganisms. Microorganisms are bacteria and yeasts that are not visible to the human eye. In fact, microorganisms are all around us. They are in the water we drink, the food we eat and the air we breathe. But most comforting fact is about 95% of microorganisms are good for us. Microorganisms, sometimes called microbes, include bacteria, viruses, fungi, yeasts, algae and protozoa.
What is Intestinal Microflora
- The microorganisms that live in our intestines make up what is called the intestinal micro flora. The intestinal microflora is made up of many types of bacteria, fungi and yeast. These microflora are main cause of infections in body but they give the body immense positive effects and make our life a healthy & beautiful.
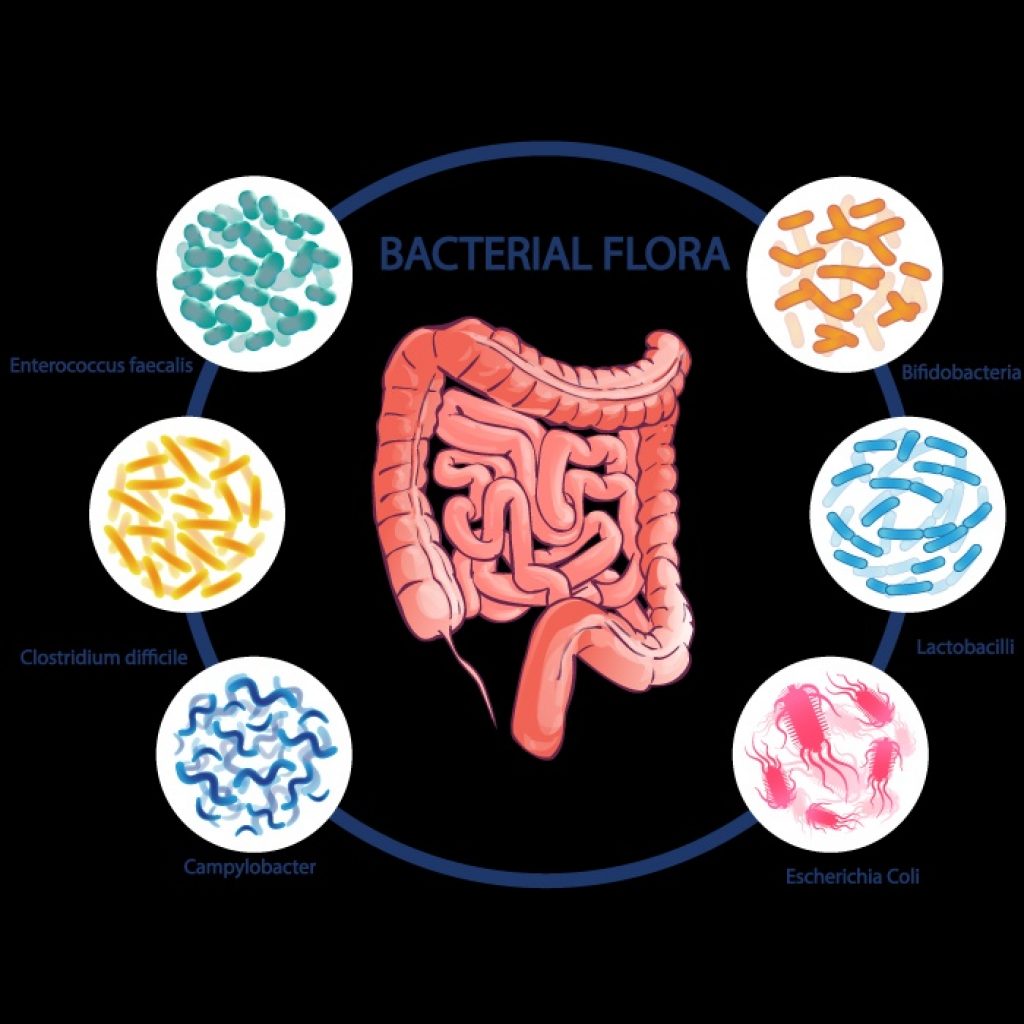
- In body, there are over 400 different species of microbes, living in symbiosis with our body their host. Bacteria can be found in mouth, stomach, intestines and urogenital tract. Some bacteria found in our body are known to be beneficial to human health and are called probiotics. Meanwhile, the other bacteria in body, which are harmful, are called pathogenic bacteria.
- Depending on the type of bacteria, there is a different effect on the body bacteria. It can have healthy, e.g., immune-boosting, benefits or cause toxicological (poisoning) harm to the body. A careful balance is necessary for health. The growth of harmful microbes in body can result in disease.
Gut Microbes influence the internal environment
- The 400 species of microbes living in body are fighting for space. They want to live, thrive and reproduce in intestinal tract, an environment that offers the ideal temperature, humidity and food sources. These microbes create different environment in the Gut , acidic or alkaline for their growth .
- The battle for production of the suitable climate is continuous depending on the type of microbes taking control .There are good microbes and there are bad microbes which has constant battle for the resources of the body. Two examples of bad microbes commonly found in the human body are the bacteria E. coli and the yeast Candida albicans.
- Bad microbes flourish in an alkaline environment. Many of them produce ammonia to change the pH of the intestinal tract to be more alkaline and thus enhance their ability to survive and flourish. Stress and diet can also influence the presence of these microbes. Keeping these bad microbes in control is vital to the body’s health.
Enter Probiotic in the story
The good microbes are called probiotics. Probiotics have a positive impact on the body’s health. They prefer a more acidic intestinal environment. Many of the probiotics are called lactic acid bacteria.
They can secrete lactic acid into their environment, making it more acidic and thus more hospitable to them. Stress and diet can reduce the number of probiotics in the intestinal tract.
Luckily, as most childhood tales of good versus evil end in a positive light, so does this story. In a healthy body the majority of the microflora in the intestines is good bacteria, also known as probiotics.
Microflora is unique to body
Just as each of us has unique fingerprints, we also have a unique mix of intestinal microbes. The makeup of intestinal microflora began to take shape at birth. Then depending on whether we were breast or bottle fed, different types of microbes were added. Over time, individual diet, environment and lifestyle choices have shaped and personalized the microflora.
Key to healthy Microflora
- The key to a healthy microflora in body is to maintain a large number of good microbes in digestive tract. An overwhelming balance of good over bad bacteria is important. Several factors can negatively affect this balance these include aging, depressed immunity, digestive tract infections, environmental pollution, poor diet, stress and diarrhoea.
- Use of antibiotics affect the microflora. We live in a world filled with antibiotic and antibacterial products. We have become bacteriophobic. The focus has been on fighting “bad” bacteria. The result is a loss of not just bad bacteria but good bacteria, including probiotics. Without probiotics we can become ill.
- The normal ratio of probiotics to harmful microbes should be approximately 85% to 15%. This balance of good to bad can be disrupted by stress, a poor diet or infection by a bad microbe. If there is an overgrowth of bad microbes (pathogens) in body, antibiotics may be necessary to regain balance. For example, irritating throat can be caused by an overgrowth of a nasty bacteria. If same not treated with antibiotics, runs the risk of developing into a serious infection.
- Antibiotics might seem like a good idea, but using them further disrupts microflora. Antibiotics not only destroy the bad bacteria, which are causing you to be sick, but they also destroy good bacteria living in the digestive tract. Both antibiotics and antibacterial products can cause an imbalance in our body’s microflora by reducing the number of probiotics.
- When the composition of the intestinal microflora is disrupted, there can be negative effects on the health of the body. As such, it may be necessary to reestablish body’s probiotic population.
- The intestinal microflora can be replenished and restored to its healthy strength and balance by taking probiotic supplements and eating probiotic-enriched foods. Yogurt, supplements and many foods offer an easy source of probiotics to help regain the balance.
Probiotics |Good Microbes i.e. bacteria of Gut |Elixir of good health
- The term probiotic is derived from Greek and means ‘for life’ as opposed to antibiotics which means ‘against life’. The history of probiotics began with the consumption of fermented foods.
- Definition of Probiotics “live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host. “Medically, probiotic is defined as microorganisms that positively affect the health of our body when administered in adequate amounts.
- A probiotic offers a health benefit to the host. The intestinal microflora has the metabolic activity potential equal to that of the liver, we always underestimate the metabolic activity initiated and completed by intestinal microflora.
- Perhaps the greatest health benefit that probiotics offer is the promotion of a healthy immune system. The intestines are lined with cells called epithelial cells. These are the same cells that make up skin. Epithelial cells are specially designed to help the body carefully interact with its environment.
- When we eat food it contains a lot of foreign things, including bacteria, pesticides and preservatives which interact with the epithelial cells that line the intestinal tract. This interaction can be negative or positive. If the pesticide we ate interacts with intestinal epithelial cells and the body decides it is a foreign invader an immune reaction will occur in an attempt to rid the body of this invader. This a negative interaction.
- When probiotics attach to receptor sites on the epithelial lining of the intestinal wall, the interaction is positive. Probiotics send communications to nearby immune cells. This has positive effects on the immune system that can affect the entire body.
- Clinical and population studies have shown this interaction between microbes in our intestinal tract, the epithelial cells and eventually the immune cells to be beneficial in the body. In fact, the ability of microbes to positively affect the immune system is known to help prevent illness and to be helpful in the treatment of certain allergic, inflammatory and chronic diseases.
- Probiotic health benefits include aiding in proper digestion , inhibiting pathogenic microbes, promoting a healthy immune system; and helping with some vitamin production.
- Probiotics affect many aspects of the body including nutrient digestion and absorption, immunity and much more. Probiotics aid digestion by completing the breakdown of food that was not fully digested. A good example is the ability of certain strains of probiotics to help with the digestion of lactose in the small intestine. As well, probiotics strains found in the colon help with digestion of some forms of fiber. They also produce vitamins, including the particularly important B vitamins, which play a key role in energy metabolism.
Probiotics helping in immune system
- Playing a key role in the maturation of the immune system. The intestinal tract is sterile at birth but eventually hosts 1014 CFU/mL (CFU stands for colony-forming units, a measurement of how many living groups of probiotics are present) of microbes representing between 400 and 500 species.
- The intestinal microflora develops gradually as we age and is influenced by factors including our mother’s microflora and our diet, use of antibiotics, stress, hygiene, environment and possibly genetics.
- We know that probiotics play an important role in the maturation of the immune system from scientific studies on a germ-free animal model. In a germ-free animal, there are no microbes living in the intestinal tract. The lack of microbes was associated with a greatly underdeveloped immune system. In other words, if there are no microbes in an intestinal tract, the immune system does not develop fully. Probiotics are very important to immune health.
- There are many health benefit offered by probiotics to the host improved digestion, immunity and health.
Choosing a Probiotic species
Which probiotic species is right for you? You can choose a probiotic based on its preferred location to inhabit in the body or by your age requirements. For example, Lactobacilli love to live in the small intestine and Bifidobacterium love to live in the colon.
In some disease conditions, researchers know which specific c species offers health benefits. However, there is much research left to be completed. If choosing a probiotic strain based on its effects Experts agree that having a healthy mixture of a variety of probiotic species in the intestinal tract can provide the best health benefits. In other words, multi-species probiotics may be the right choice for you.